Insulated pipe supports sit in between the pipe itself and the pipe clamp or clips, to maintain thermal performance. One of the main types of insulated pipe supports, phenolic foam blocks, work to prevent thermal conduction which can result in heat loss and an increase in energy usage.
Insulated pipe supports isolate the pipework from the pipe clamp to limit heat transfer and thermal bridging. It also allows for a continuous vapour barrier to be carried through the support system.

There are three main types of insulated pipe supports:
Wood blocks were the preferred material for insulating supports for a long time. In recent years, however, the use of wooden pipe support inserts has dwindled. This is likely due to the updated British Standard for insulated pipe supports, BS5970:2012 which now gives the view that “wooden pipe supports should not be used”.
Wood blocks do not offer a reasonable thermal bridge between the outer works and the pipe. There is an increased risk of condensation forming on wooden blocks and they are ineffective at maintaining vapour barriers.
Phenolic foam pipe insulation blocks are a very effective alternative to woodblocks and have rapidly become the number one preferred insulated pipe support material.
Independent thermal analysis has shown that the use of phenolic insulated pipe support inserts can reduce heat loss through the supports of +75°C LTHW systems by up to 10x when compared to woodblock inserts. This is in addition to the benefits of phenolic in maintaining the vapour barrier and limiting heat gain on systems operating below ambient temperature.
Phenolic insulation is also much more cost-effective than wood, calcium silicate or foam glass alternatives due to a higher insulation value.
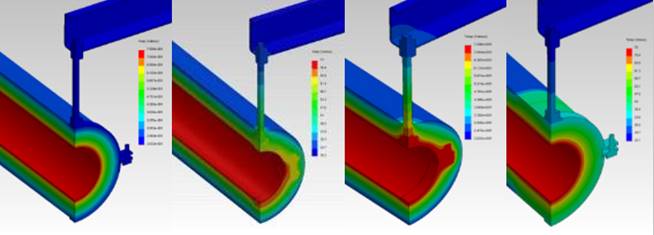
The image below demonstrates the rate of heat loss on (from left to right) phenolic pipe support, a rubber-lined clip fixed to pipe, a metal clip fixed to pipe, woodblock pipe support.
Typically, calcium silicate insulation is used where pipe temperatures exceed 250°F. Therefore, the usual places you’ll find this type of insulation include chemical plants, refineries, and steam electric power plants.
As previously mentioned, there is a British Standard – BS5970 – which was updated in 2012. This is a code of practice relating to the thermal insulation of pipework, ductwork, associated equipment and other industrial installations. The 2012 update included a few significant changes.
One change being that the code of practice no longer permits the use of wooden block pipe supports due to them providing an ineffective vapour barrier and having poorer thermal properties than the alternatives.
In addition, the standard recommends that the pipe support bracket being fixed over the load-bearing insulation is of the same material (or compatible with) the insulation on the pipe.
Walraven’s phenolic foam pipe insulation supports (Phenblox) are CE marked in accordance with EN14314:2009 + A1:2013. They are tested and guaranteed compatible with our main unlined  clamp ranges.
clamp ranges.
Our blocks are made from high-density phenolic foam with the best available thermal insulation properties. They are CFC and HCFC-free and classified as Zero ODP (ozone depletion products). To guarantee the technical properties of our phenolic, each batch is also tested in accordance with ISO 9001:2015.
In addition to this, Walraven Phenblox’ have a special bore coating, which eradicates any possibility of pipe corrosion on copper pipes. They are also manufactured with stepped joint faces to ensure vapour seal and accurate placement.
Our Technical Team has created load tables showing the maximum allowed load for Walraven Phenolic and clip combinations.
As well as manufacturing phenolic insulation blocks, we also manufacture all of the individual components that, when used together, create the complete pipe support system. This includes parts such as:

Although Walraven Phenblox’ can be used in conjunction with other components, there are some advantages to using the complete Walraven system, a couple being: